What is skin cancer?
Actinic keratosis
Also known as Solar keratosis.
Actinic keratosis is a precursor to skin cancer.
Symptoms:
- Often extensive UV-induced superficial dysplasia.
- Often found on sun-exposed areas of elderly persons, especially on the face, scalp, chest, and arms.
- Increased risk in persons with fair skin and prolonged UV exposure.
- Red, scaly, and sometimes thickened lesions.
Treatments:
- Cryosurgery
- Curettage
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT)
- Topical treatment
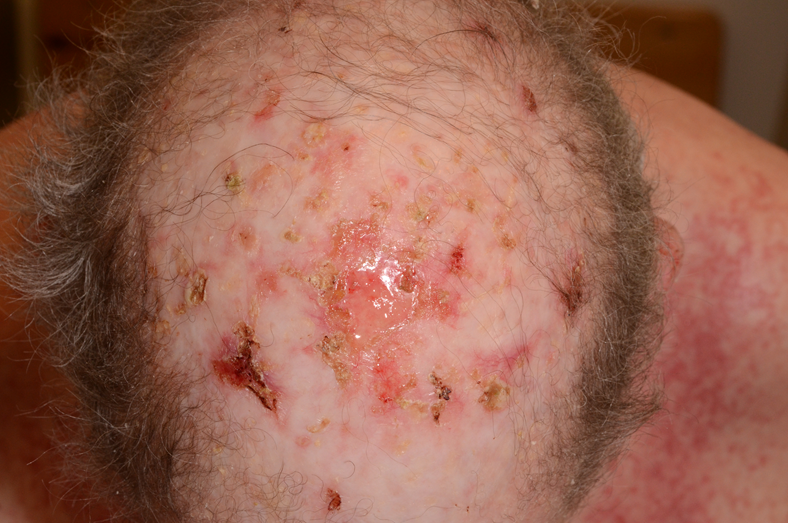
Case: 75-year-old golfer
The patient has red, scaly, itching lesions on the scalp.
The patient has no history of skin cancer.
Suggested treatment:
Photodynamic therapy or topical treatment due to dissiminated sun damage of the skin.
Basal cell carcinoma
Also known as Rodent ulcer and basalioma.
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of non-melanoma skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common cancer, with more than 15,000 new annual cases in Denmark.
Symptoms:
- Slow-growing locally invasive tumor.
- Often localized in the head and neck area and upper body of UV-exposed people with fair skin.
- Shiny/pearly smooth nodule with central ulceration and rolled edges or irregular slight scaly plaque with micro-erosions.
Treatments:
- Mohs micrographic surgery
- Conventional surgery
- Superficial radiotherapy
- Photodynamic therapy
- Cryosurgery
- Topical treatment
- Electrochemotherapy
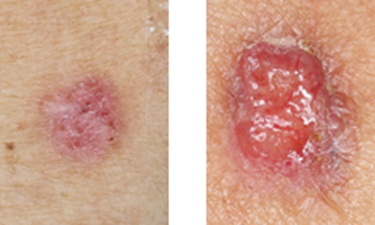
Be cautious about these warning signs:
1. Non-healing ulcers.
2. Long-lasting red scaly patches.
3. Long-lasting nodules with raised boarders.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Also known as: Planocellulært karcinom and spinocellulært karcinom
Squamous cell carcinoma is a type of non-melanoma skin cancer with approximately 3.000 new annual cases in Denmark. This cancer is characterized by a fast-growing invasive tumor with a low risk of metastasizing.
Symptoms:
- Localized to sun-exposed areas in older individuals with sun-damaged skin, especially around the scalp and face.
- Increased risk in patients with fair skin type, suppressed immune system, and prolonged UV exposure.
- Tender, warty ulcerated or hyperkeratotic nodules.
Treatment:
- Excision
- Superficial radiotherapy
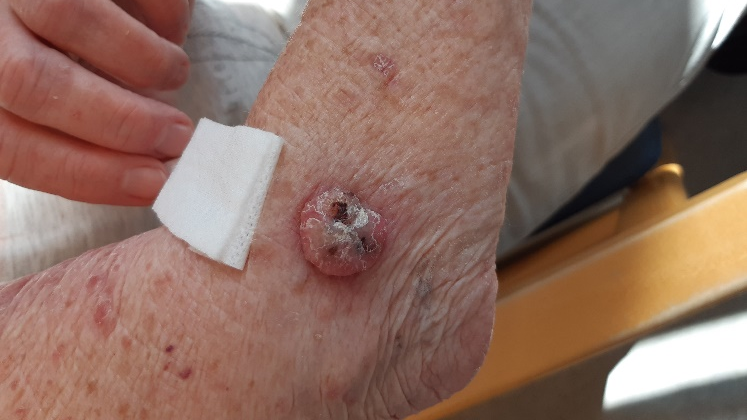
Case: 77-year-old women with multiple actinic keratoses
The patient has fair skin and a long history of sun tanning.
The patient has had multiple previous cases of non-melanoma skin cancer.
Suggested treatment is surgery.